What are Stem Cells?
Stem cells are nothing but “Master Cells” that generate other differentiated cell types. Each tissue within the body contains a unique type of stem cells that renew and replace that tissue (e.g. nerve, brain, cartilage, blood) when needed due to damage or wear and tear.
Stem cells of the blood (hematopoietic stem cells) produce all other blood cells in the human body, including red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells. Sources of hematopoietic stem cells include umbilical cord blood, bone marrow, peripheral blood and embryos.
In other simpler words, stem cells are the body’s “master” cells because they give rise to all other tissues, organs, and systems in the body. The stem cells’ ability to differentiate, or change, into other types of cells in the body, is a new discovery that holds tremendous promise for treating and curing some of the most common diseases such as heart disease, cancers, stroke, Alzheimer‘s and many others.
So, now the question comes, what is so special about these stem cells? Stem cells have the remarkable power to develop into many different cell types in the body.
Basically, these cells serve as a sort of repair system for the body; they can theoretically divide without limit to replenish other cells as long as the person or any other living being is still alive.
When a stem cell divides, each new cell has the power to either remain a stem cell or become another type of cell with a more specialized function, such as a muscle cell, a red blood cell, or a Cell of brain. Undoubtedly, this is unique about stem cells.
There are three classes of stem cells:
- Totipotent: A fertilized egg is considered totipotent, meaning that its potential is total; it gives rise to all the different types of cells in the body.
- Multipotent: Stem cells that can give rise to a small number of different cell types are generally called multipotent.
- Pluripoten: Pluripotent stem cells can give rise to any type of cell in the body except those needed to develop a fetus.
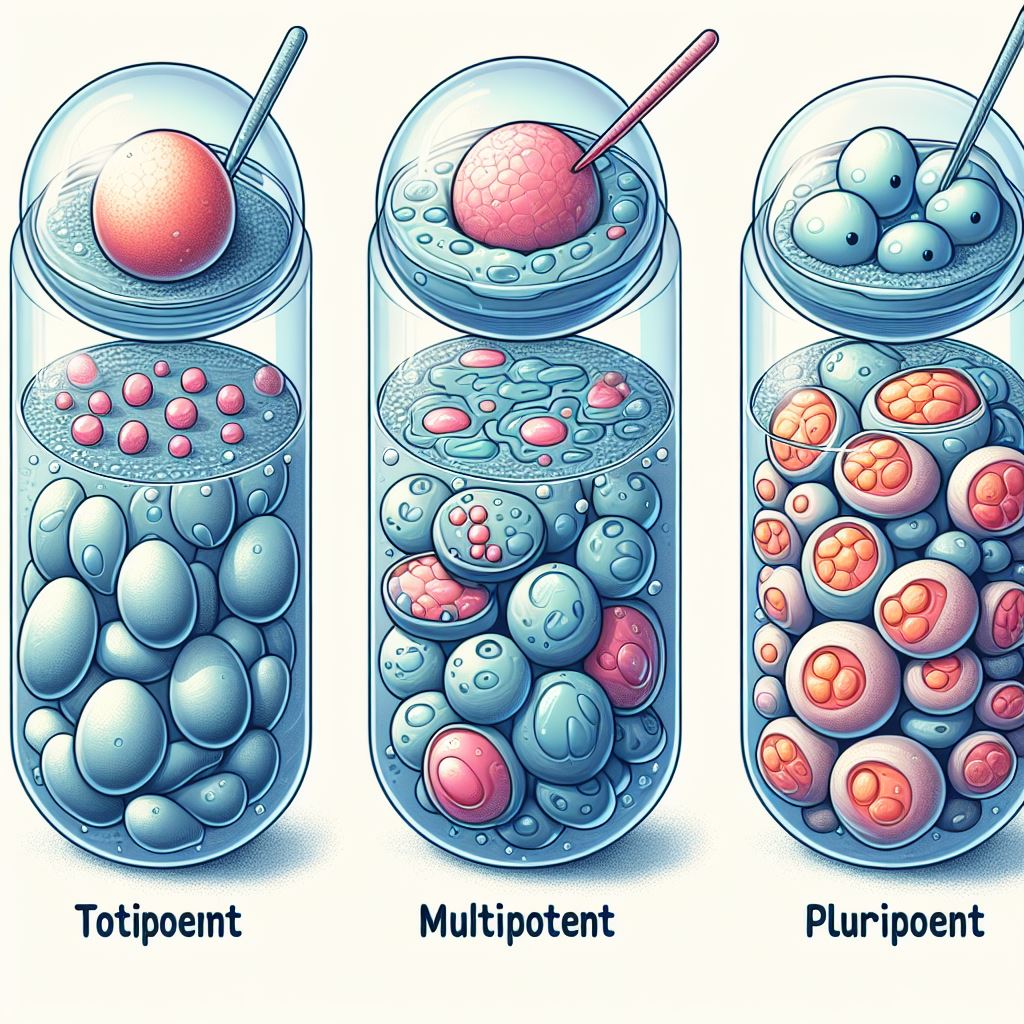
Simply put, stem cells are primitive cells that give rise to other types of cells. Also called progenitor cells, there are several typs of stem cells.
Totipotent cells are considered the “master” cells of the body because they contain all the genetic information needed to create all the cells of the body plus the placenta, which nourishes the human embryo.
Human cells have this potentiality only during the first few divisions of a fertilized egg. After 3 – 4 divisions of totipotent cells, there follows a series of stages in which the cells become increasingly specialized.
The next stage of division results in pluripotent cells, which are highly versatile and can give rise to any cell type except the cells of the placenta.
At the next stage, cells become multipotent, meaning they can give rise to several other cell types, but those types are limited in number.
An example of multipotent cells is hematopoietic cells—blood stem cells that can develop into several types of blood cells, but cannot develop into brain cells.
At the end of the long chain of cell divisions that make up the embryo are “terminally differentiated” cells (cells that are considered to be permanently committed to a specific function).
Day-old human embryos are used to isolate pluripotent stem cells. Pluripotent stem cell “lines”—cell cultures that may be cultured in the lab indefinitely—can be produced from the embryos’ cells. Additionally, fetal tissue (older than 8 weeks of development) has been used to produce pluripotent stem cell lines.
Not long ago, scientists and researchers firmly believed that the differentiated cells couldn’t be altered or caused to behave in any way other than the way in which they have been naturally committed. New research, however, has even called that assumption into question.
Researchers have been able to get blood stem cells to act like neurons, or brain cells, in recent stem cell tests.. Scientists now believe that stem cell research could reveal far more vital information about our bodies than was previously known .
In addition, it was recently discovered that some stem cells also occur in the bodies of adults, rather than exclusively in embryos (which indeed a big breakthrough, because of many controversies of embryos stem cells amongst various social groups).
Many kinds of multipotent stem cells have been discovered in adults, and scientists believe that many more will be discovered.
Research is now being conducted on both adult and embryonic stem cells to determine the characteristics and potential of both to cure disease. So future seems to be quite bright in this field.
